Configuring network settings is one of the first steps you will need to take on Windows Server 2016. Whether you are using the GUI or Core version, changing the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and DNS Servers can be done in different ways depending on the case.
In today’s article, you will see how to change the basic IPv4 network settings for your machine’s adapters using the GUI, PowerShell, SConfig, and command prompt.
Configure network settings using the graphical user interface
Ok, the process is more than simple, but I mention it to make the article more complete.
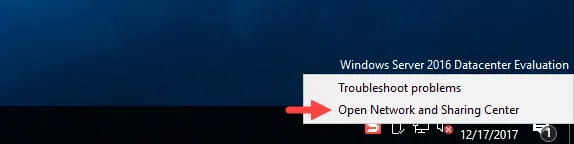
Right-click the network icon in the notification area, and then click Open Network and Sharing Center.
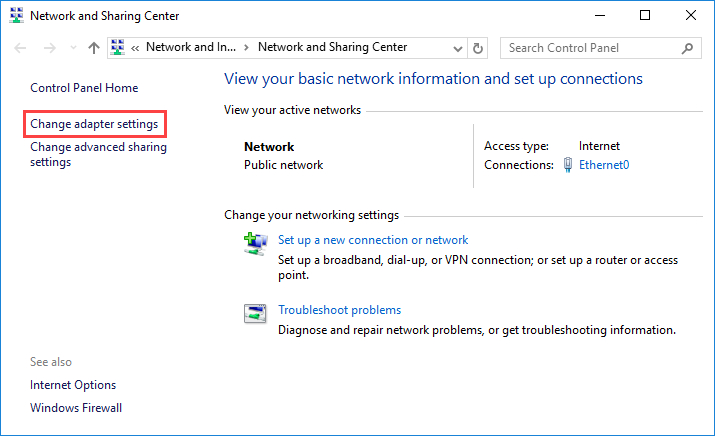
In the window that opens, click Change adapter settings to display the available network adapters of the machine.
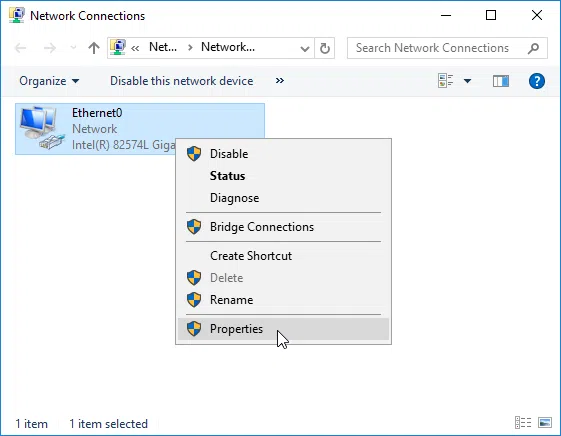
Right-click the adapter you are about to change the IP settings and then click Properties.
Click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP / IPv4) and then the Properties button.
Here, enable Use the following IP address and enter the static IP addresses for the server, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS servers.
That’s it!
Configure network settings using PowerShell
First, we need to identify the InterfaceIndex number for the network adapter we want and then based on that, we will proceed to set it up.
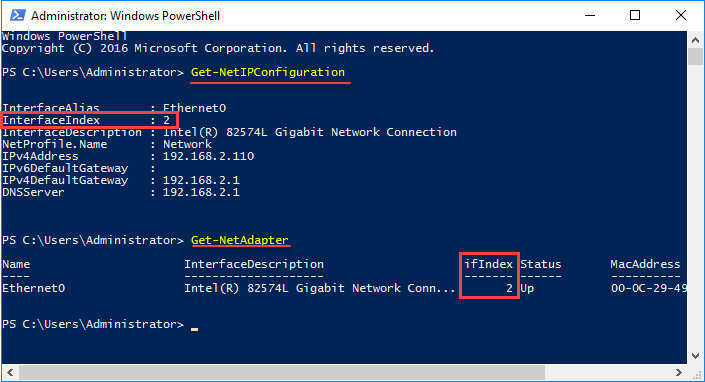
By typing the Get-NetIPConfiguration cmdlet you can see the current IP settings of all the network adapters of the machine. Note the InterfaceIndex.
Alternatively, type the Get-NetAdapter cmdlet to see the available network adapters. Note the number again in ifIndex.
To set the IP address, the Subnet (PrefixLength) and the Default Gateway, type the following command by changing the addresses according to your own network.
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceIndex 2 -IPAddress 192.168.2.100 -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway 192.168.2.1 |
To set up DNS servers, use the following Set-DnsClientServerAddress command.
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceIndex 2 -ServerAddresses 192.168.2.10, 192.168.2.11 |
You can use the Get-NetIPConfiguration cmdlet again to confirm that it has declared the correct settings.
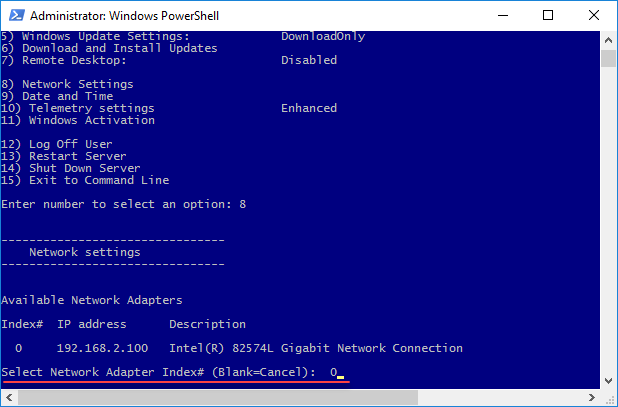
Configure network settings using the SConfig tool
For a more interactive process, you can use the SConfig tool through PowerShell. Type SConfig and press Enter.
To change the network settings, type the number 8 that corresponds to Network Settings.
Type the index number of the adapter you want to set up.
Then use Options 1 and 2 to set the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and the adapter’s DNS servers. I do not think I need to go further into this piece, it’s pretty easy and intuitive.
Configure network settings using the Command Prompt
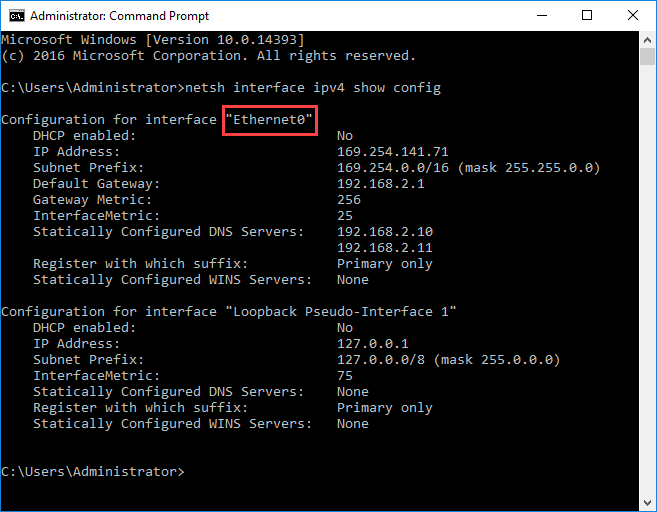
In this case, we will use the netsh command.
First, run the following command to note the name of the adapter you are going to set up. In our case is Ethernet0.
netsh interface ipv4 show config |
To change your IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway, type the following command by changing the addresses according to your own settings.
netsh interface ipv4 set address name = "INTERFACE NAME" static IP_ADDRESS SUBNET_MASK GATEWAY |
For example, it will be something like this.
netsh interface ipv4 set address name = "Ethernet0" static 192.168.2.100 255.255.255.0 192.168.2.1 |
Next, to configure the Primary DNS Server, use the following command.
netsh interface ipv4 set dns name = "INTERFACE NAME" static DNS_SERVER |
For example, it will be something like this.
netsh interface ipv4 set dns name = "Ethernet0" static 192.168.2.10 |
To configure the Secondary DNS Server, use the following command.
netsh interface ipv4 set dns name = "INTERFACE NAME" static DNS_SERVER index = 2 |
Similarly to the previous example.
netsh interface ipv4 set dns name = "Ethernet0" static 192.168.2.11 index = 2 |
Finally, you can use the first command again to confirm that your settings are correct.