Let’s assume the following scenario: We have a Domain Controller on the network that has ceased to work for some reason that we don’t care about at this point. We have no backup, and it will not work again, so we will need to completely remove it from the infrastructure.
To achieve this, we must implement a forced removal of the Domain Controller from Active Directory. Furthermore, because such an action leaves some orphaned metadata in the AD, we will need to clean up these metadata. In case the DC is somewhat online, the first action is to try to demote it from AD.
We will deal with this scenario in this article. Let’s move on.
Forced removal of a Domain Controller from Active Directory
The forced removal of a DC can be done in 3 ways. Using the Active Directory Users and Computers console, Active Directory Sites and Services console, and the NTDSUtil command-line tool.
When you use the two consoles, Microsoft claims that the orphaned metadata is automatically cleaned. However, as you will see, there are still some records of the deleted DC, especially on the DNS console and Sites and Services. Although DNS scavenging removes them, personally, when I delete a DC, I do a quick check of all DNS objects to confirm and delete all the remaining records.
Using the Users and Computers console
Open the Active Directory Users and Computers console and go to the Domain Controllers OU. Here, right-click the DC to be removed and then Delete.
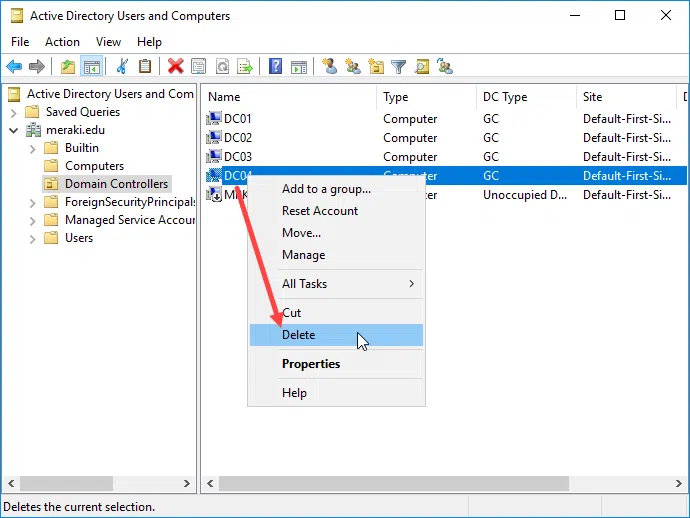
Confirm the deletion by pressing Yes.
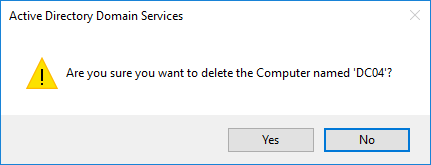
Immediately afterward, you will see a message informing you that you are about to remove a Domain Controller without using the classic method we have described in an earlier article. If DC is not going to go back online again, you need to select the Delete this Domain Controller anyway. It is permanently offline and can no longer be removed using the removal wizard option, and then click the Delete button.
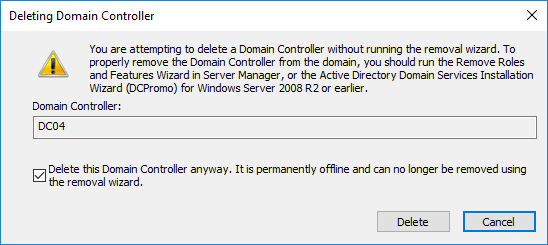
If the DC you are deleting was also a Global Catalog (GC) server, click Yes to confirm the deletion.
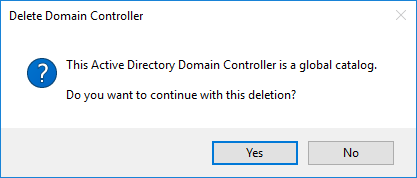
If the DC you delete had one or more FSMO roles, click OK to transfer them to another DC. This is if you have not already seized them yourself.
Using Active Directory Sites and Services console
Open the Active Directory Sites and Services console, expand the Sites object till you find the DC you want to delete. Here, right-click the NTDS Settings icon on the DC, and then click Delete.
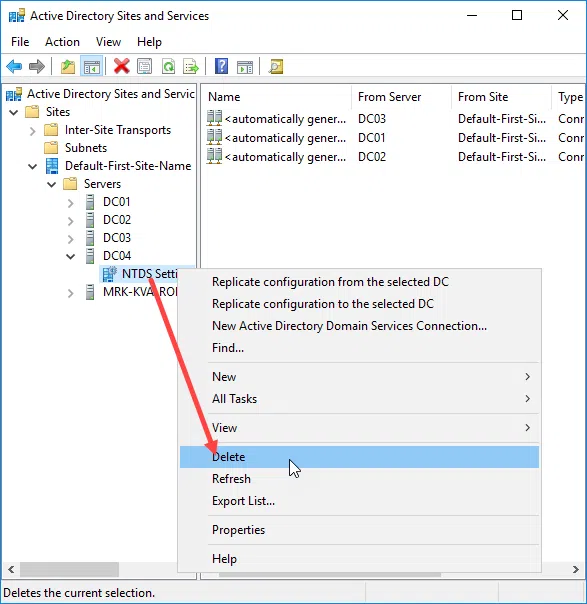
Confirm the deletion by pressing Yes.
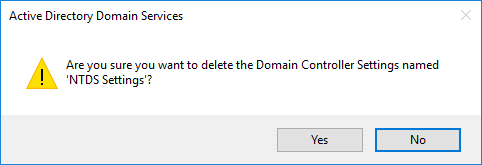
Confirm again while accepting the warnings by clicking the Delete button.
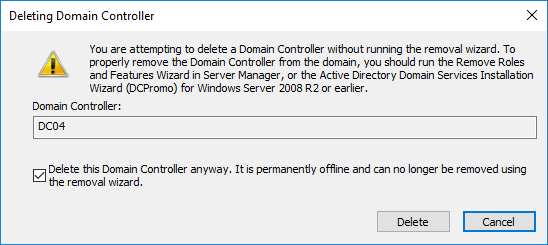
As before, if DC was also Global Catalog and/or had at least one of the FSMO roles, you will need to confirm the deletion.
You can then delete the DC object in the Active Directory Sites and Services console.
Using the NTDSUtil tool
First, open the command line or PowerShell with administrator privileges.
Type ntdsutil and press Enter.
Type metadata cleanup and press Enter.
Type connections and press Enter.
Type connect to server <-servername> and press Enter. Where <-servername>, is the name of a working DC in the same domain.
Type quit and press Enter.
Type select operation target and press Enter.
Type list domains and press Enter.
Type select domain <-number> and press Enter. Where <-number>, the corresponding number to the domain that the non-functional DC member was a member of.
Type list sites and press Enter.
Type select site <-number> and press Enter. Where <-number>, the number that corresponds to the site that the non-functional DC member was a member of.
Type list servers in site and press Enter.
Type select server <-number> and press Enter. Where <-number>, the number that corresponds to the DC you want to remove.
Type quit and press Enter.
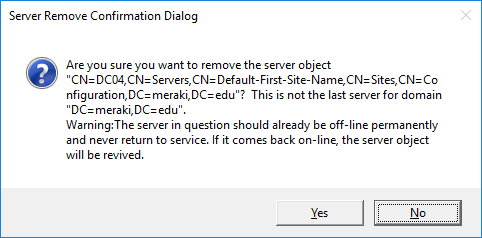
Type remove selected server and press Enter.
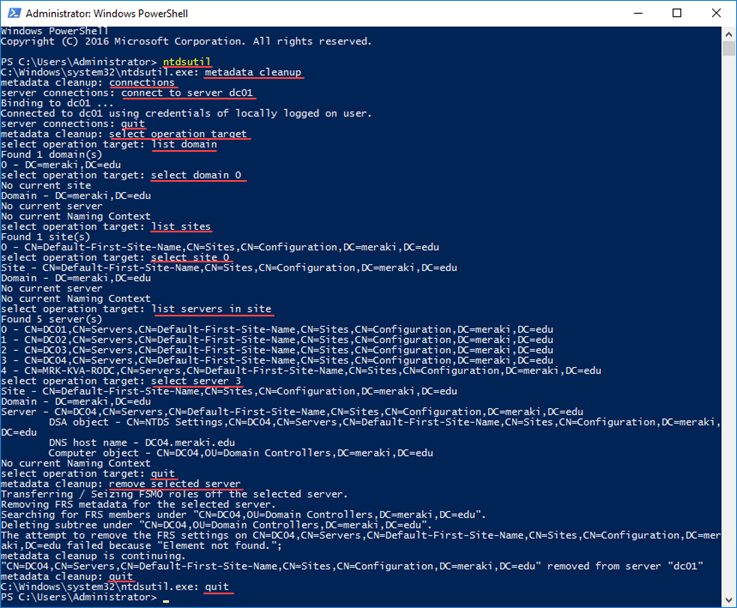
In the confirmation window that appears, click Yes to continue the deletion process.
Finally, type quit and press Enter to exit the NTDSUtil management environment.
After completing the steps above, do not forget to check all DNS objects to delete any records of the removed DC.




Καλησπέρα Δημήτρη,
Αντιμετωπίζω ένα πρόβλημα με έναν demoted DC που έχει μείνει στα Sites and Services, και φυσικά με repadmin /replsummary.
Ο server έχει γίνει κανονικά demote αλλα είναι up καθως είναι file server.
Με τη διαδικασία του NTDSUtil και ειδικότερα με το “Server Remove Confirmation Dialog” τον διαγράφεις οριστικά απο DC ή τον διαγράφεις ΚΑΙ σαν object απο το AD;
Αν τον διαγράφεις και σαν object εφόσον ο server πρέπει να συνεχίσει να υπάρχει σαν object μήπως θα πρέπει να προχωρήσω με τη διαδικασία χρησιμοποιόντας την Active Directory Sites and Services console;
Καλησπέρα Κώστα. Θα προτιμούσα να γράφεις στα αγγλικά για να μπορούν να διαβάζουν όλοι οι επισκέπτες τα σχόλια.
Η παραπάνω διαδικασία γίνεται ΜΟΝΟ στην περίπτωση που έχεις ‘χάσει’ τον DC και δε πρόκειται να επανέλθει στο δίκτυο. Οπότε, τον διαγράφει από DC και σαν object από το AD.
Για να κάνεις ένα ‘απλό’ demote από DC σε member server που θα συνεχίσει να είναι παραγωγικός, ακολουθείς αυτή τη διαδικασία.
what if I have a seperate child domain (with single DC) and is no more accessible. removed from everywhere but still showing in partitions. when trying to delete from root server saying can not delete a leaf object. when trying to delete the name index giving error again saying replication has not completed for 1 time.
Hi abhishek, you can check you child to ADSIEdit.
Connect to your AD then select “Configuration”.
ADSI Edit
>Configuration[sample.contoso.com]
>CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com
>from this three, look for “Partition”.
>Check child DC partition and try to delete.
Once delete complete. Run repadmin /showrrepl
To remove Domain Controller the above 3 steps will be helpful.After you removed domain controller .Is it Possible to add same domain controller in a Domain.If Possible please help me by providing steps .Thanks for sharing this article
cionssystems
Honestly, this is one of the best manuals I have read this month. Thank you!
saved my life love u
Thanks!
look forward to your next post
Excellent info, fixed my client’s server issue. Thank you!!!